
1. DEFINITIONS
Phonology studies the abstract side of the sound of a language, the phonemes. It studies the following area:
- The phonemic system: the number of phonemes and their relationship to others.
- Phoneme sequences and syllable structure: combinatory possibilities and relations on the sequence of phonemes that are used.
- Suprasegmental phonology:
- Stress.
- Intonation.
The phoneme is the smalllest contrastive lingüistic unit which may bring out a change of meaning. It is possible to establish the phonemes of a language by means of a process of communication or the dicovery of minimal pairs.
Phonetics:
- Articulatory phonetics.
- Acoustic phonetics.
- Auditory phonetics.
2. RECEIVED PRONUNTIATION
RP developed among the better-off members of society from the Early Modern English period in the triangle formed by the cities of London, Cambridge and Oxford. Moreover, it was adopted by the Court and the upper classes and, in the age of the radio and television, by the B.B.C.
Standard English is the grammar of the most prestigious variety of English. It is used in England, Scotlan, Wales and Northern Ireland besides other parts of the world.
Internacional English Pronuntiation is a tipe of pronuntation that is not from any particular geographical area.
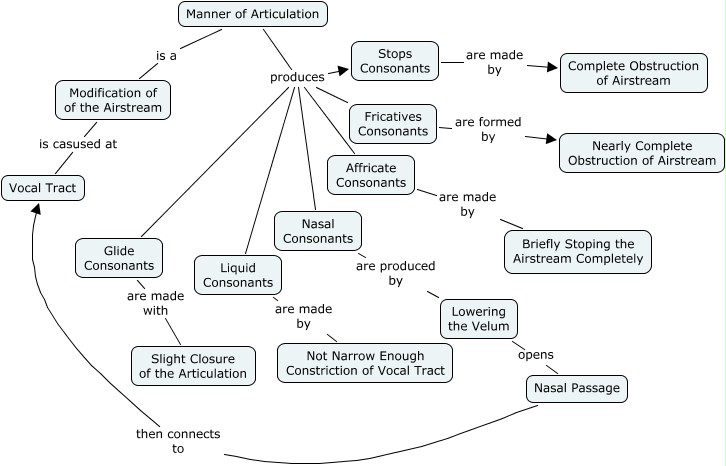
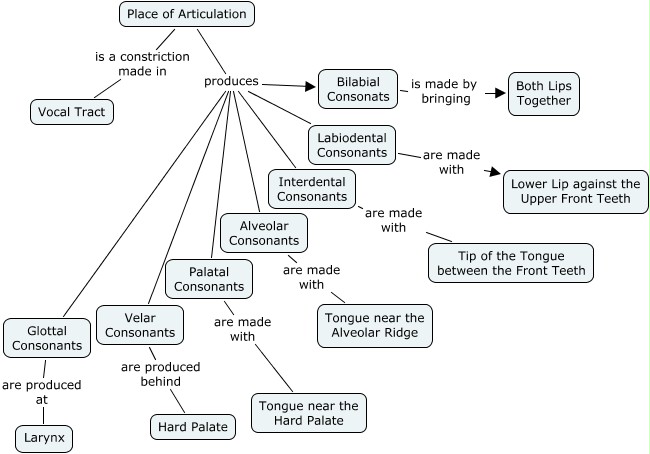
3. THE ARTICULATORY ORGANS

Upper surface:
-Upper lip.
- Upper teeth.
- Alveolar ridge: a small bump behind the upper lip and the upper teeth.
- Hard palate: a bony structure.
- Soft palate or “velum”: a kind of flexible muscular.
- Uvula: a fleshy protuberance.
- Pharynx wall: right at the back of the mouth, is involved in some sounds.
Lower articulations:
- Lower lip.
- Lower teeth.
- Tongue: the most important articulation due to his flexibility.
- Tip: when the tongue is at rest this is normally just behind or slightly above the bottom teeth.
- Blade: is under the alveolar ridge.
- Front: under the hard palate.
- Centre: under the hard palate.
- Back: under the soft palate.
- Root: under the soft palate.
- Epiglottis: below the root of the tongue and opposite the pharyngeal wall. It is a flap of eartilange which is lowered during swallowing.

5. ENGLISH VOWELS

5.1. DIPHTHONGS
.gif/250px-RP_vowel_chart_(diphthongs).gif)